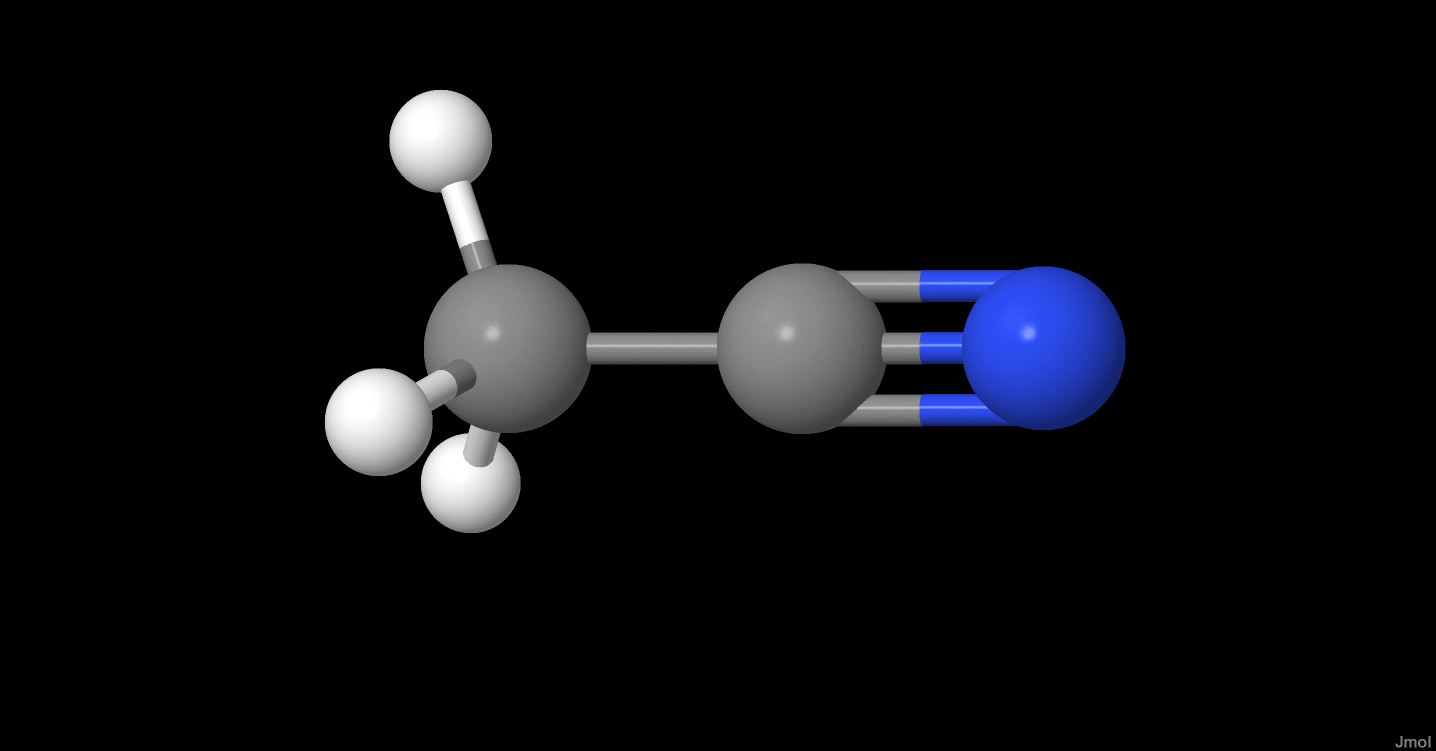
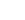CH3CN
Click on the icon info to get details.
Species data
| Common Formula | CH3CN |
| Stoichiometric Formula | C2H3N |
| Name | Acetonitrile |
| Mass | 41.02655 a.m.u |
| Charge | 0 |
| CAS | 75-05-8 |
| Inchi | InChI=1S/C2H3N/c1-2-3/h1H3 |
| InchiKey | WEVYAHXRMPXWCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| State | Ground State
|
ISM Abundance
| log10 Abundance | Reference | Source Name | Source Type | Link |
|---|
Polarizability
| Evaluation | Definition | Value (Å3) | Method | Origin | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| total | 4.48 | Measurements | Bibliography | Lide, D. R.. ;2000; |
|
Definition: total Value (Å3): 4.48 Method: Measurements Origin: Bibliography Reference: Lide, D. R.. ;2000; |
Dipole moment
| Evaluation | Value (D) | Method | Origin | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.92519 | Measurements | Bibliography | Lide, D. R.. ;2004; |
|
Value (D):
3.92519 Method: Measurements Origin: Bibliography Reference: Lide, D. R.. ;2004; |
Enthalpy of formation
| Evaluation | T (K) | Value (kJ.mol-1) | Method | Origin | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 81.09 ±0.37 | Reviews and Evaluations | Database : Burcat | ||
| 298 | 74.04 ±0.37 | Reviews and Evaluations | Database : Burcat | ||
| 298 | 64.4 | Measurements | Database : CCCBDB (http://cccbdb.nist.gov/) | ||
| 0 | 71.5 | Measurements | Database : CCCBDB (http://cccbdb.nist.gov/) |
|
T (K): 0
Value (kJ.mol-1) : 81.09 ±0.37 Method: Reviews and Evaluations Origin: Other database Reference: |
|
T (K): 298
Value (kJ.mol-1) : 74.04 ±0.37 Method: Reviews and Evaluations Origin: Other database Reference: |
|
T (K): 298
Value (kJ.mol-1) : 64.4 Method: Measurements Origin: Other database Reference: |
|
T (K): 0
Value (kJ.mol-1) : 71.5 Method: Measurements Origin: Other database Reference: |
Desorption energy
| Evaluation | Emean (K) | Emin (K) | Emax (K) | Pre-exponential factor (s-1) | Order factor | Method | Origin | Reference | Type of surface | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4680 ±1404 | 0 | 0 | 0.00E+0 | 1 | Calculations | Bibliography | Wakelam, V. et al. ;2017;ArXiv e-prints;, | H2O | To estimate the unknown binding energies (for most of the radicals for example), we have developed a model founded on the stabilization energy of the complex between the various species and one water molecule. Then, we assume that the binding energy of the species with ASW is proportional to the energy of interaction between this species and one water molecule. To determine the proportionality coefficients, we fit the dependency of the experimental binding energies versus the calculated energies of the complexes for 16 stable molecules. Uncertainties in ED is estimated to be 30%. The preexponential factor is to be computed using the Hasegawa et al. (1992) approximation. | |
| 6253 | 2.37E+17 | 1 | Reviews and Evaluations | Bibliography | Minissale, Marco et al. ;2022;ACS Earth and Space Chemistry;, | Compact Amorphous Solid Water | Uncertainties are discussed in Minissale et al. (2022) | |||
| 4954 | 2.73E+17 | 1 | Reviews and Evaluations | Bibliography | Minissale, Marco et al. ;2022;ACS Earth and Space Chemistry;, | Graphite | Uncertainties are discussed in Minissale et al. (2022) | |||
| 4680 | 0 | 0 | 0.00E+0 | 1 | Estimation | Database : OSU | H2O | This value was deduced from Collings et al. (2004). This binding energy was listed in the original OSU gas-grain code from Eric Herbst group in 2006. The pre-exponential factor is not given. It can be computed using the formula given in Hasegawa et al. (1992). |
|
Emean (K): 4680 ±1404
E min (K): 0 E max (K): 0 Pre-exponential factor (s-1): 0.00E+0 Method: Calculations Origin: Bibliography Reference: Wakelam, V. et al. ;2017;ArXiv e-prints;, Type of surface: H2O Description: To estimate the unknown binding energies (for most of the radicals for example), we have developed a model founded on the stabilization energy of the complex between the various species and one water molecule. Then, we assume that the binding energy of the species with ASW is proportional to the energy of interaction between this species and one water molecule. To determine the proportionality coefficients, we fit the dependency of the experimental binding energies versus the calculated energies of the complexes for 16 stable molecules. Uncertainties in ED is estimated to be 30%. The preexponential factor is to be computed using the Hasegawa et al. (1992) approximation. Evaluation: |
|
Emean (K): 6253
E min (K): E max (K): Pre-exponential factor (s-1): 2.37E+17 Method: Reviews and Evaluations Origin: Bibliography Reference: Minissale, Marco et al. ;2022;ACS Earth and Space Chemistry;, Type of surface: Compact Amorphous Solid Water Description: Uncertainties are discussed in Minissale et al. (2022) Evaluation: |
|
Emean (K): 4954
E min (K): E max (K): Pre-exponential factor (s-1): 2.73E+17 Method: Reviews and Evaluations Origin: Bibliography Reference: Minissale, Marco et al. ;2022;ACS Earth and Space Chemistry;, Type of surface: Graphite Description: Uncertainties are discussed in Minissale et al. (2022) Evaluation: |
|
Emean (K): 4680
E min (K): 0 E max (K): 0 Pre-exponential factor (s-1): 0.00E+0 Method: Estimation Origin: Other database Reference: Type of surface: H2O Description: This value was deduced from Collings et al. (2004). This binding energy was listed in the original OSU gas-grain code from Eric Herbst group in 2006. The pre-exponential factor is not given. It can be computed using the formula given in Hasegawa et al. (1992). Evaluation: |
Diffusion energy
No data